Your Location:Home > Products > Inorganic Chemicals > Lithium hydroxide
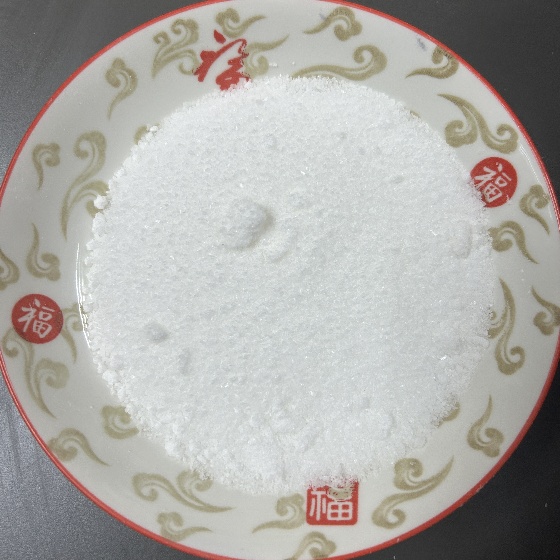


CasNo: 1310-66-3
MF: LiOH.H2O
Appearance: colourless, hygroscopic crystals
|
General Description |
Lithium hydroxide (LiOH) is a white, crystalline, inorganic compound that can be anhydrous or hydrated. It's a strong base and a weak alkali metal hydroxide that's moderately soluble in water and slightly soluble in ethanol. Lithium hydroxide is also hygroscopic and has a tendency to absorb carbon dioxide from the air. Lithium hydroxide is a strong alkaline compound. |
| Uses | Lithium hydroxide is used to absorb unwanted gas. The scrubbers use lithium hydroxide to remove carbon dioxide from the air inside the spacecraft. Used in the preparation of lithium salts of fatty acids means lithium soaps with mineral oil and other additives used to make lithium-based greases. In industry, it has important uses. For example, it is used in the production of lithium-based grease to improve the high temperature resistance of the grease. In the field of battery manufacturing, lithium hydroxide is one of the key raw materials for the positive electrode material of lithium-ion batteries, which has an important impact on the performance and life of the battery. In addition, lithium hydroxide can also be used to prepare other lithium compounds. However, lithium hydroxide is corrosive, and strict protective measures must be taken during operation and use. |
InChI:InChI=1/Li.2H2O/h;2*1H2/q+1;;/p-1/i1+0;;
Temperature programmed decomposition and complimentary microscopy/spectroscopy techniques were performed on lithium hydroxide with micron-sized grains. The lithium hydroxide grains thermally decomposed into Li2O, releasing H2O, following a three dimensional phase boundary moving from the surface inward.
In this study, a bipolar membrane electrodialysis (BMED) process was developed to convert lithium phosphate into lithium hydroxide and phosphoric acid. To verify the feasibility of BMED in lithium phosphate conversion, effects of solubility, current density and concentration of phosphate on the separation performance were investigated.
Lithium hydroxide monohydrate based ther...
The energy barriers measured for the decomposition of surface and near-surface lithium hydroxide are noticeably smaller than those of bulk counterpart. The conversion of Li2O grains back to lithium hydroxide during moisture exposure was also found to proceed from the surface inward such that surface states are filled before bulk states.
water

lithium hydroxide
lithium carbonate
n-butyllithium
lithium 4-(methyl(phenylsulfonyl)amino)-benzoate

water
oxygen
Nitrogen dioxide